Table of Contents
Introduction
Canadian enterprises are accelerating their cloud transformation initiatives in 2026. As businesses scale across provinces and global markets, relying on a single cloud provider is no longer enough. Downtime, compliance mandates, and vendor lock-in risks are pushing organizations toward a smarter approach — a Multi-Cloud Kubernetes Strategy for Canadian Enterprises.
Kubernetes has become the backbone of modern cloud-native applications. However, running Kubernetes across multiple cloud platforms requires thoughtful architecture, strong governance, and disaster recovery planning — especially in a highly regulated environment like Canada.
In this guide, we’ll explore how Canadian organizations can design resilient multi-cloud Kubernetes environments, maintain regulatory compliance, and implement enterprise-grade disaster recovery strategies.
Why Canadian Enterprises Are Moving to Multi-Cloud Kubernetes
Across Canada, industries such as fintech, healthcare, SaaS, and e-commerce are modernizing their infrastructure. Several drivers are influencing this shift:
1. Avoiding Vendor Lock-In
Relying solely on one cloud provider can limit flexibility. A multi-cloud setup ensures workloads can move between platforms like Azure, AWS, or Google Cloud without disruption.
2. Data Residency & Sovereignty Requirements
Canadian data protection regulations often require sensitive data to remain within national borders. Multi-cloud architecture enables businesses to keep data in Canadian regions while maintaining global redundancy.
3. Business Continuity & High Availability
Outages can cost enterprises millions. Multi-cloud Kubernetes clusters reduce downtime risks by distributing workloads across multiple regions.
4. Performance Optimization
Different cloud providers offer strengths in networking, AI services, or cost efficiency. A hybrid approach allows companies to optimize workloads based on performance needs.
Designing a Multi-Cloud Kubernetes Architecture
Implementing a Multi-Cloud Kubernetes Strategy for Canadian Enterprises requires a structured architectural approach.
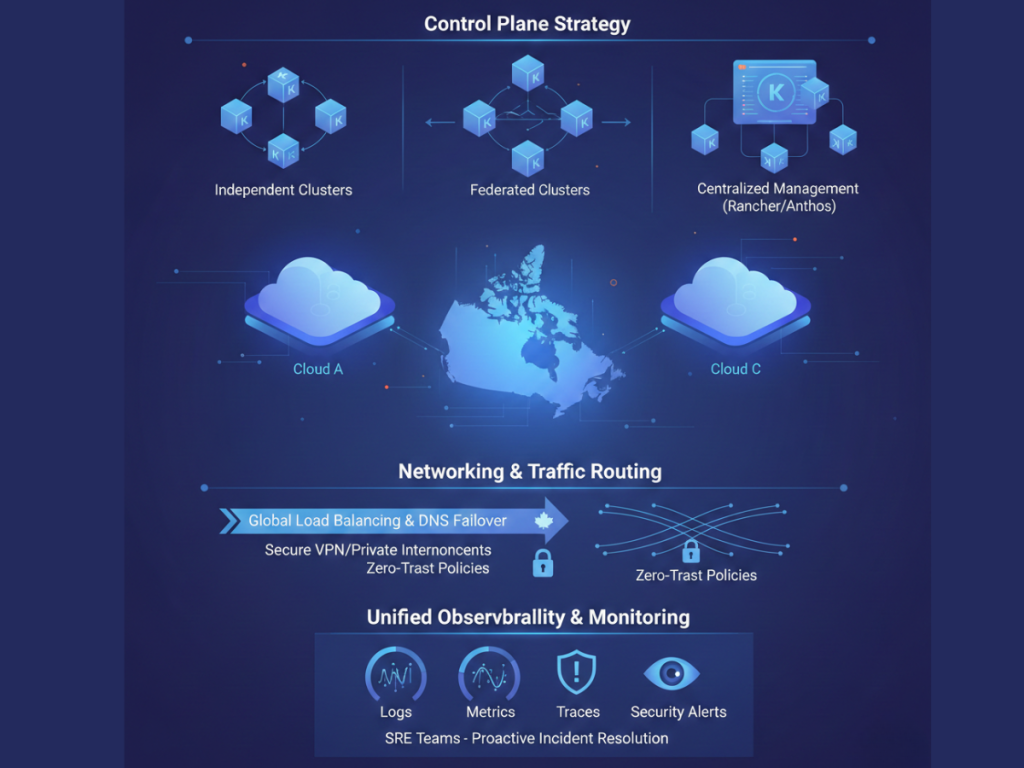
1. Control Plane Strategy
Organizations typically adopt one of these models:
- Independent clusters per cloud
- Federated Kubernetes clusters
- Centralized management with tools like Rancher or Anthos
Each approach depends on scale, compliance needs, and operational maturity.
2. Networking & Traffic Routing
Multi-cloud networking must support:
- Global load balancing
- DNS-based traffic failover
- Secure VPN or private interconnects
- Zero-trust network security policies
Many Canadian enterprises deploy traffic routing solutions that automatically direct users to the nearest healthy cluster.
3. Unified Observability & Monitoring
Visibility is critical. Enterprises must centralize:
- Logs
- Metrics
- Traces
- Security alerts
This enables Site Reliability Engineering (SRE) teams to proactively resolve incidents before customers are affected.
Compliance & Data Governance in Canada
Compliance is one of the most important components of a Multi-Cloud Kubernetes Strategy for Canadian Enterprises.
Key Considerations:
- Data residency within Canadian regions
- Encryption at rest and in transit
- Role-based access control (RBAC)
- Audit logging
- Secure secrets management
Industries such as financial services and healthcare must align with national and provincial data regulations. Kubernetes clusters must be configured with strict security policies, network segmentation, and automated compliance scans.
Infrastructure as Code (IaC) tools help ensure consistent, compliant cluster deployments across multiple clouds.
Kubernetes Disaster Recovery Strategy
Disaster recovery is not optional in 2026. A well-designed Multi-Cloud Kubernetes Strategy for Canadian Enterprises includes a robust DR framework.
1. Define RPO & RTO
- Recovery Point Objective (RPO) – Maximum acceptable data loss
- Recovery Time Objective (RTO) – Maximum acceptable downtime
These metrics guide your replication and backup strategy.
2. Active-Active vs Active-Passive Clusters
Active-Active Model
- Traffic distributed across multiple clusters
- Automatic failover
- Higher infrastructure cost
- Near-zero downtime
Active-Passive Model
- Secondary cluster remains standby
- Activated during outage
- Cost-efficient but slower recovery
3. Backup & Restore Best Practices
- Regular etcd backups
- Persistent volume snapshots
- Cross-cloud replication
- Automated restore testing
Canadian enterprises often overlook disaster recovery testing. A DR strategy is only effective if tested quarterly.
Real-World Example: Canadian Fintech Expansion
Let’s consider a Toronto-based fintech company expanding across North America.
The Challenge:
- Strict Canadian data residency laws
- High transaction volumes
- Zero tolerance for downtime
- Seasonal traffic spikes
The Solution:
They implemented a multi-cloud Kubernetes setup:
- Primary cluster in Azure Canada region
- Secondary cluster in AWS Canada region
- Cross-cloud data replication
- Global traffic routing
- Centralized monitoring
The Result:
- 99.99% uptime
- Seamless failover during a regional outage
- Full compliance with Canadian financial regulations
- Improved customer trust
This real-world scenario demonstrates how a structured Multi-Cloud Kubernetes Strategy for Canadian Enterprises delivers measurable business value.
Role of SRE in Multi-Cloud Kubernetes
Site Reliability Engineering (SRE) plays a crucial role in ensuring performance and stability.
Key SRE practices include:
- Error budget tracking
- Automated incident response
- Infrastructure automation
- Continuous performance testing
SRE teams ensure Kubernetes environments remain resilient, scalable, and secure across cloud providers.
Security Best Practices for Multi-Cloud Kubernetes
Security should be embedded from design to deployment.
Recommended Practices:
- Zero-trust architecture
- Pod security standards
- Image vulnerability scanning
- Network policy enforcement
- Multi-factor authentication
- Regular penetration testing
Security automation tools reduce human error and ensure policy enforcement across clusters.
Cost Optimization in Multi-Cloud Environments
Multi-cloud doesn’t mean uncontrolled spending.
Enterprises can optimize costs through:
- Autoscaling clusters
- Spot instances
- Resource quotas
- Rightsizing workloads
- FinOps monitoring
A strategic architecture balances redundancy with cost efficiency.
Future Trends for 2026
Canadian enterprises are expected to adopt:
- Edge-native Kubernetes clusters
- AI-driven cluster optimization
- Policy-as-code compliance frameworks
- Cross-cloud service mesh architectures
Businesses that proactively adopt these innovations will remain competitive in Canada’s evolving DevOps market.
Conclusion
A modern Multi-Cloud Kubernetes Strategy for Canadian Enterprises is no longer a luxury — it’s a necessity.
By combining:
- Thoughtful architecture
- Strong compliance governance
- Enterprise-grade disaster recovery
- Continuous monitoring and automation
Canadian businesses can build infrastructure that is resilient, secure, and future-ready.
As cloud complexity grows in 2026, organizations that invest in multi-cloud Kubernetes strategies will gain operational flexibility, regulatory confidence, and competitive advantage.
Strengthen Your Multi-Cloud Kubernetes Strategy Today
Downtime and compliance risks can cost more than you think. Build a secure, resilient, and compliant multi-cloud Kubernetes environment tailored for Canadian enterprises.
Get a Custom Architecture & DR Assessment. Future-proof your infrastructure with expert guidance.
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. Why do Canadian enterprises need multi-cloud Kubernetes?
Multi-cloud Kubernetes reduces downtime risk, improves compliance with data residency laws, and prevents vendor lock-in.
2. How does multi-cloud improve disaster recovery?
Workloads can automatically fail over to a secondary cloud environment if one region experiences an outage.
3. Is multi-cloud more expensive?
While infrastructure costs may increase, proper architecture and FinOps practices ensure optimized spending.
4. How does Kubernetes support compliance in Canada?
Kubernetes enables RBAC, encryption, audit logging, and policy enforcement to meet regulatory standards.
5. What industries benefit most from this strategy?
Fintech, healthcare, SaaS, government services, and e-commerce companies benefit significantly from multi-cloud deployments.

